Mining solutions
Sustainable mining of natural resources is a cornerstone for our standard of living and prosperity. Mined materials have a wide array of applications. They play a critical role in construction (e.g., building frameworks) and power generation, and are used as commodities and minerals for industrial applications. They contribute to current green technologies – like wind turbines, solar panels, and electric vehicles – and the exploration of new exploitable deposits as part of the effort to counter climate change. And they are used to produce luxury goods. To play a positive and sustainable economic role in society, mined metals and minerals must be explored for, extracted, transported, and processed according to quality control processes that deliver safe and high-quality products. A wide array of Anton Paar instruments can contribute to every step of this development and production chain.
| Instrument | Samples | Measurement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
High temperature viscometer and
rheometer:
|
|
Rheometry |
Coal combustion for energy production: Find out the temperature
and composition at which a predefined viscosity (viscosity for flow down
the reactor wall) is reached
|
 |
Inline Density
Meter:
|
|
Concentration Measurement |
Platinum mining: Concentration measurement of HCl,
HNO3, and diluted H2SO4 in the PMR
|
 |
Inline Sound Velocity
Concentration Meter:
|
|
Concentration Measurement |
Gold mining: HCl dilution control for calcium removal (carbon
regeneration)
Gold mining: Lixiviant concentration measurement (Au-leach)
Uranium mining: H2SO4 concentration
measurement (U-leach)
Uranium mining: Oxidant concentration measurement (U-leach)
Uranium mining: NaOH precipitant concentration measurement
(U-leach)
Platinum mining: H2SO4, NaOH,
Na2SO4 concentration measurement (BMR, PMR)
Copper mining: H2SO4 concentration
measurement (acid plant)
Nickel mining: H2SO4 concentration
measurement (acid plant)
|
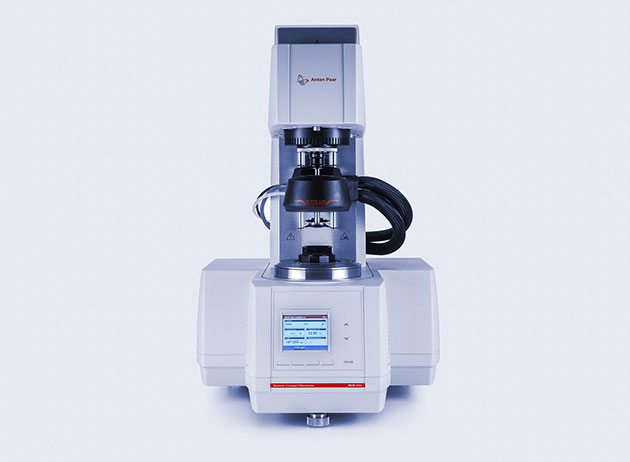 |
Modular Compact Rheometer:
|
|
Rheometry |
Hydraulic fracturing: Predict the flow behavior of the mixture of
water, chemicals and sand used for fracking at high pressures and
various shear rates
Slurry transport (ore and tailings): Analyze and lower the yield
point of ore slurry to avoid downtime of the processing plant and assure
an efficient transportation process
Slurry storage (ore and tailings): Determine the necessary shear
rate to keep mineral particles suspended during storage
Dilution of tailings slurry: Efficiently dilute tailings to
enable pumping, while minimizing discarded material
|
 |
Hot block digestion
system:
|
|
Hot Block Digestion |
Refinining, extraction, smelting (=purification) of various ores:
Perform digestion of lead prill after fire assay or fusion process with
48 digestion positions at once
Quality control: Perform digestion of lead prill after fire assay
or fusion process with 48 digestion positions at once
Environmental control of mining site and refining site: Analyze
water and soil (48 samples at once) for contamination with harmful
elements
|
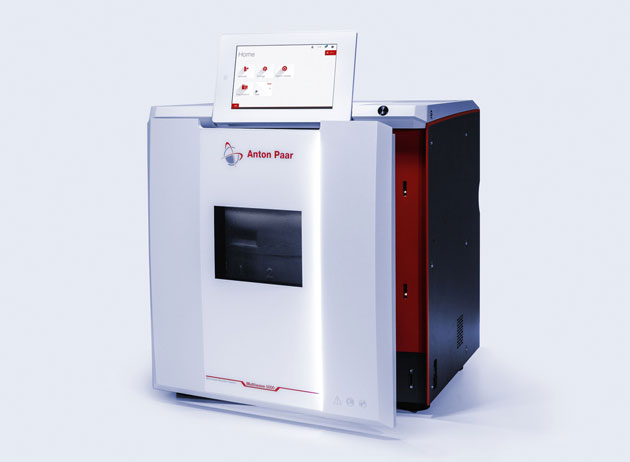 |
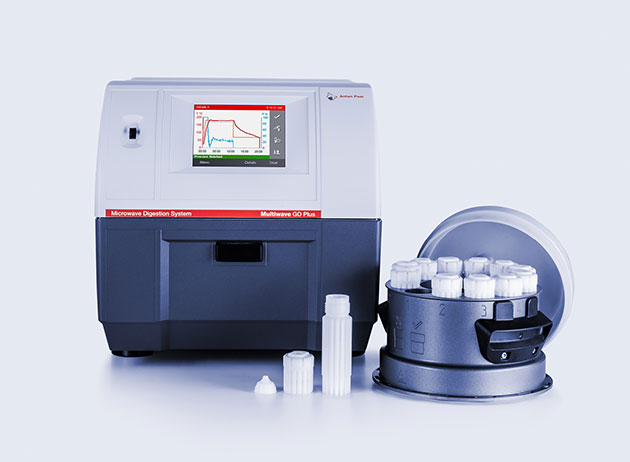
Microwave digestion
system:
|
|
Microwave Digestion |
Exploration of possible mining sites: Analyze metal content in
mineral samples from exploration
Sludge analysis: Perform
robust and easy-to-use acid digestion of sludge prior to environmental
trace analysis of toxicologically and environmentally relevant elements
(ICP, AAS, etc.).
|
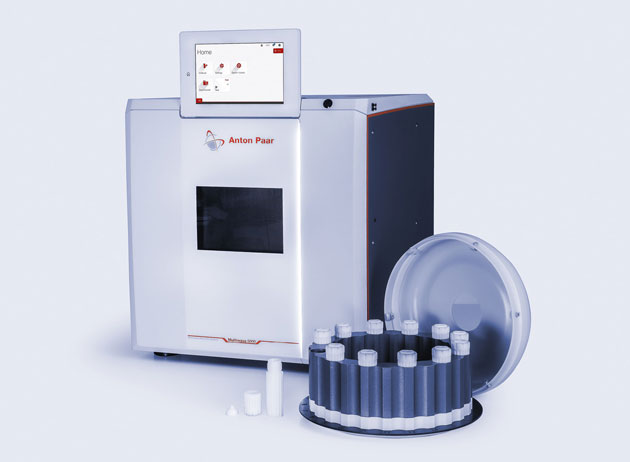 |
Microwave digestion
system:
|
|
Microwave Digestion |
Mining and excavation: Dissolve rocks containing elements of
interest prior to subsequent analysis (ICP, AAS, etc.)
Refinining, extraction, smelting (=purification) of various ores:
Perform fast and trouble-free acid digestion with high throughput,
without contamination or loss of analyte
Quality control: Perform fast and trouble-free acid digestion
with high throughput, without contamination or loss of analyte
Caustic leaching of bauxite: Simulate the industrial Bayer
process on a lab scale to determine optimum conditions for the
industrial process
Extraction, refining and quality control of coal and graphite:
Reliably digest highly reactive samples such as coal, coke and graphite,
which require high temperatures
|
 |
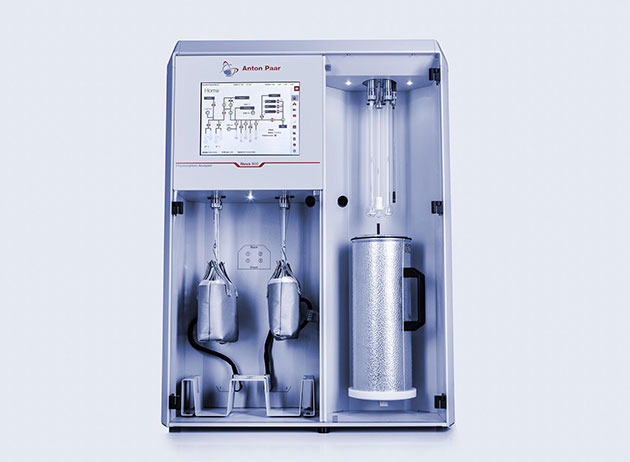
Microwave digestion
system:
|
|
Microwave Digestion |
Exploration of possible mining sites: Analyze metal content in
mineral samples from exploration
Waste water
quality determination: Perform microwave digestion on waste
water so that it is ideally prepared for further elemental analysis
|
 |
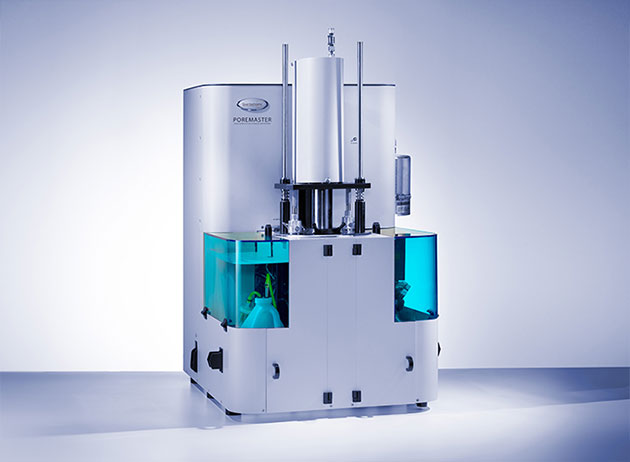
Surface area and pore
analyzers:
|
|
Vacuum Volumetric Gas Sorption Analysis |
Slurry stabilization: Calculate the proper amount of
dispersant/stabilizer to reduce costs by eliminating unnecessary, excess
dispersant/stabilizer
|
 |
Mercury intrusion pore size
analyzers:
|
|
Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry |
Site evaluation: Evaluate groundwater movement and pollution by
quantifying pore size
|
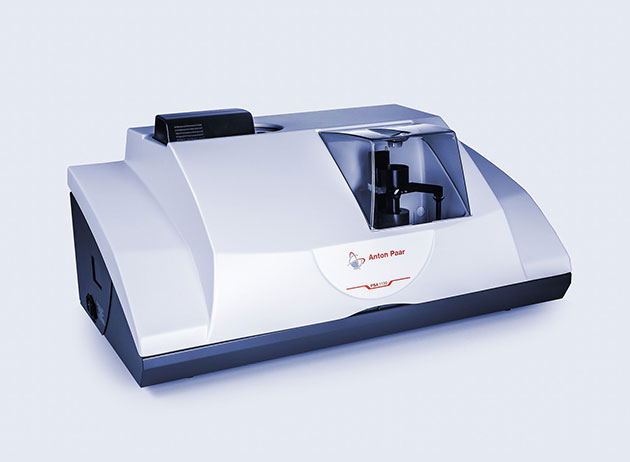 |
Particle size
analyzer:
|
|
Laser Diffraction |
QC of drilling fluids: Maximize the (re)usage of drilling muds by
detecting low-gravity solids (LGS) as they build up, via monitoring of
particle size distribution (PSD)
Ore grinding: Prevent energy wastage on unnecessary grinding, by
determining and thus eliminating fine and ultrafine particles
Ore grinding and separation: Produce uniform particle size to
prevent ore separation bias, via particle size optimization to control
the separation behavior
Quality control of processed ore: Determine and monitor the
particle size distribution of processed ore to ensure consistent quality
of the final product
|
 |
Rotational
Rheometer:
|
|
Rotational Rheometry |
QC of drilling fluids: Smoothly transport drilling muds via
determination of viscosity at rest and during pumping of bentonite
|
 |
Powder Cells for
MCR:
|
|
Powder Rheometry, Rheometry |
Ore transport: Avoid issues during transport and storage of
powdery materials by simulating mechanical transport
Processed ore transport: Improve the pneumatic transport of
processed powders by determining fluidization behavior
|
 |
Single-station gas pycnometers
for true density:
|
|
Gas Pycnometry |
Site evaluation: Evaluate groundwater movement and pollution by
quantifying rock porosity
Formulating well cement: Calculate target solid % and improve
accuracy of Blaine measurement, to produce a cement with proper support
and thermal insulation
Formulation of drilling fluids: Obtain the optimum density for
hydrostatic pressure and circulation
Ocean transport of ore fines: Perform safety calculations to
avoid loss of vessel at sea via evaluation of the risk of liquefaction
for a particular load
Settling tank/pond/basin design: Calculate the sedimentation
times of tailings/washings for more efficient operation and lifecycle
management to reduce overall costs and land use
Froth flotation (separation of beneficial minerals): Optimize the
slurry concentration from pulp density by determining the size and
number of flotation cells for a given capacity
Coal washability test: Maximize the economics of separating coal
from rock and minerals by optimizing the density of fluids in float-sink
tanks
Quality control, packaging and transportation: Receive the
correct volume of pulverized rock (ore)
Tailings dam safety: Measure the density of dry tailings,
saturated tailings, fines and slime for improved risk assessment
Waste gypsum: Determine the suitability of recovered waste
material for use in mortars, and calculate formulation
|
 |
Rotational
viscometer:
|
|
Rotational Viscometry |
QC of drilling fluids: Smoothly transport drilling muds via
determination of viscosity at rest and during pumping of bentonite
|
 |
Automated Multipurpose Powder
X-Ray Diffractometer:
|
|
X-Ray Diffraction |
Exploration: Optimize the mining process and effectively plan
downstream processing requirements by identifying high-value deposits
and the mineral forms present
Exploration: Discover possible recovery losses ahead of time, to
optimize the extraction process, by identifying non-extractable ore
forms
QC and grade control: Increase efficiency and stabilize plant
conditions by selecting the optimal grade
Ore processing: Optimize the operational efficiency of the mining
process and the beneficiation process of the ore by rapidly analyzing
the qualitative and quantitative mineral composition of the mined
material
Ore processing: Reduce the costs and environmental impact of ore
processing by identifying the iron oxidation state via phase analysis of
the mineral ore
Quality control: Continuously monitor the processed ore quality
in order to quickly respond to changes
Tailings analysis: Reduce wastage and potential environmental
damage by identifying compounds of value that can be recovered from
tailings
|
