Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) can come in different forms: amorphous, crystalline, or as different crystalline forms of the same API (polymorphs). All of these parameters influence the final product’s properties, (e.g., bioavailability, efficacy, hygroscopicity, and stability). X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a non-destructive experimental technique which provides insights into the structure of raw materials or even finished products. It is frequently applied in research and quality control to ensure the correct polymorph is produced and to investigate the amorphous amount in a sample. Additionally, non-ambient XRD is used to investigate the stability of drug formulations under varying temperature or humidity levels.
Identifying and quantifying polymorphs
Polymorphs are different crystal structures of the same compound, which can have varying physical and chemical properties. In the pharmaceutical industry, polymorphs are crucial because they affect a drug’s solubility, stability, and bioavailability. XRD is the primary technique to identify and characterize polymorphic forms, providing precise data on a compound's crystal structure.

XRD for polymorph identification
XRD identifies different polymorphic forms by analyzing the diffraction patterns of samples. Each polymorph produces a unique pattern, allowing researchers to differentiate between forms. This information helps ensure that the correct polymorph is used in drug formulation, preventing issues with drug stability or efficacy.

Case studies: Impact of polymorph identification
In a case study, it was discovered that switching to a more stable polymorph increased the shelf life of a critical medication. Another case demonstrated how early polymorph identification using XRD prevented bioavailability issues, ultimately enhancing drug performance in clinical trials.
Role of XRD in drug formulation

In the pharmaceutical industry, XRD is a critical tool in formulation development, offering detailed insights into the crystalline structure of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients. By using XRD, drug formulations can be optimized to enhance bioavailability, stability, and overall therapeutic performance.
Optimizing crystalline forms for bioavailability
The crystalline structure of a drug greatly influences its solubility and bioavailability. Different polymorphs may exhibit varying dissolution rates, influencing the drug’s absorption in the body. XRD is used to characterize and select the ideal polymorphs of an API for optimal therapeutic efficacy.
Controlling polymorphism in formulation
A key consideration in drug formulation, polymorphism is a phenomenon in which crystals composed of the same molecules adopt different structures. Formulation processes can unintentionally induce polymorphic transitions that affect drug stability or efficacy. By monitoring these changes using XRD, it is ensured that the desired form remains consistent throughout production and patient use.
Ensuring stability and shelf life
XRD is invaluable in evaluating the stability of drug formulations over time. By tracking changes in the diffraction patterns, scientists can detect subtle shifts in the crystalline structure that may occur during storage, potentially affecting the drug's shelf life. With early detection allows, adjustments can be made to the formulation or packaging to maintain the stability and potency over the intended shelf life.
Excipient compatibility and interaction monitoring
In addition to being used to analyze API polymorphs, XRD is employed to examine the interactions between active ingredients and excipients, which are inactive substances that support the drug. Incompatibilities between excipients and APIs may result in undesirable reactions, such as the formation of new crystalline phases or amorphous regions, potentially impacting the drug's performance. By identifying and preventing such issues, XRD ensures the formulation remains stable and effective.
Guiding amorphous formulations
For drugs where solubility is limited by the crystalline form, amorphous formulations can provide a good solution. The identification and control of amorphous content in formulations are facilitated by XRD, ensuring that these less-ordered structures are properly stabilized to prevent recrystallization during storage, which could decrease drug efficacy.
XRD for manufacturing consistency
XRD in the pharmaceutical industry is widely used during the manufacturing process to ensure that each batch of pharmaceuticals meets stringent quality standards. This technique ensures consistency, detects impurities, and monitors critical quality attributes of pharmaceutical products.

Ensuring consistency and purity
XRD ensures that the crystalline or amorphous structure of drugs remain consistent across all production batches. By analyzing diffraction patterns, manufacturers can confirm that each batch is identical to its predecessor. This helps to maintain drug efficacy, as any alteration in the crystalline form can impact solubility, stability, and bioavailability.
Detecting contaminants
The high sensitivity of XRD ensures that minor changes in the sample, caused by unintended chemical interactions or foreign particles, can be detected. This early detection prevents defective batches from being released to the market and ensures compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Verifying batch uniformity
Uniformity between batches is a non-negotiable requirement in pharmaceutical manufacturing. XRD enables manufacturers to quickly compare the diffraction patterns of new batches with reference standards, ensuring structural integrity and purity remain consistent throughout production. By maintaining this level of control, manufacturers uphold the high-quality standards required by regulatory bodies, ensuring that each dose is safe, effective, and reliable for patient use.
Meeting regulatory requirements with XRD
XRD is not just a tool for analysis but also plays a critical role in regulatory compliance. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA require detailed documentation on the crystalline structure and polymorphs of drug compounds. XRD data provide robust evidence to support regulatory filings, ensuring that a drug meets safety, efficacy, and quality standards. For new drug applications or variations in existing drugs, XRD helps demonstrate that the polymorphic form chosen is appropriate, stable, and consistent in its behavior.

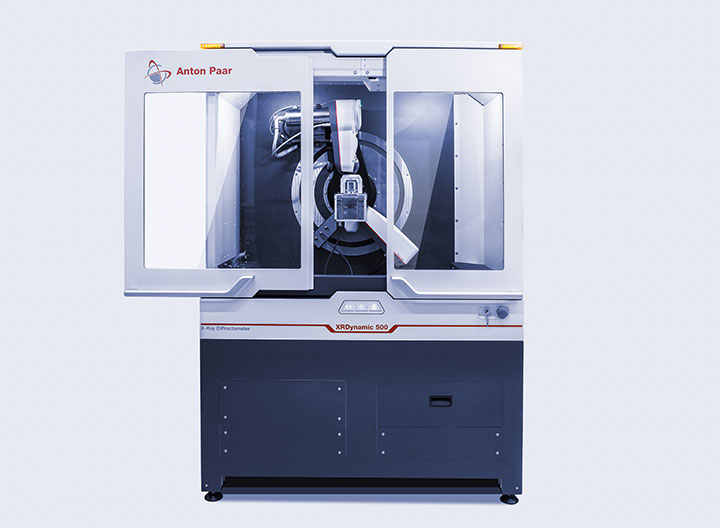
XRDynamic 500: A superior XRD solution for pharma
XRDynamic 500 is designed to meet the needs of pharmaceutical applications. Suitable for both research and manufacturing environments, it ensures compliance with FDA and EMA standards by providing consistent data and minimizing user-related errors with the highest degree of automation available on the market. Independent of the sample – crystalline, amorphous, raw material, or an entire tablet – XRDynamic 500 provides solutions to identify polymorphs, ensuring that the correct crystal structure is used to optimize bioavailability and efficacy. Its modular design allows for easy changes to the system – for example, to study the influence of humidity on the sample, which affects stability and shelf life.
Contact us today to learn more about XRD solutions for your pharmaceutical needs!
